Have you ever wondered how your PC’s GPU and other components stay cool? If you think it’s all about the fans, think again. There’s a hidden player in the game of heat management: thermal pads. These pads are crucial in drawing heat away from your components, but how exactly do they work?
In this article, we’ll break down the science of thermal pad heat conductivity and show you why they’re an essential part of keeping your hardware from overheating. Let’s dive in.
Understanding Thermal Pad Conductivity

Thermal pads come in a variety of materials, with silicon, carbon, and graphite being some of the most commonly used. Given graphite’s high thermal conductivity, as shown in the chart, it’s easy to think that graphite thermal pads would outperform all others. However, it’s not that straightforward.
Graphite thermal pads aren’t made from pure graphite. Instead, they’re often mixed with other materials. This mix makes the pads softer and more flexible, allowing them to better conform to the CPU and heatsink surfaces they’re sandwiched between.
While this flexibility is great for ensuring a good fit, it also means that the thermal conductivity of the pad is not as high as pure graphite.
The Versatile Role of Thermal Pads

Thermal pads’ flexibility and conductive materials play a pivotal role in a variety of devices, ensuring that heat is efficiently dissipated across a broad range of applications.
In graphics cards (GPUs), thermal pads are used to bridge the gap between the GPU chip and the cooling mechanism, just as they do in CPU cooling. Their ability to conform to uneven surfaces makes them ideal for use in these high-performance components, where excessive heat can lead to throttling or damage.
Similarly, in laptops and other compact electronics, where space is at a premium and cooling solutions need to be as efficient as possible, thermal pads are often found between various chips and their heat sinks or the chassis itself. This application is critical not just for CPUs and GPUs, but also for memory modules, power regulators, and other heat-generating components that benefit from improved thermal management.
Key Properties of Thermal Pads

Thermal pads come with some key features that allow them to excel in heat conductivity keeping your components cool. These include:
- Low Oil-Bleed: Thermal pads designed with low oil-bleed properties ensure that the pad does not release its constituent oils over time. This is important for maintaining the pad’s integrity and thermal conductivity. Oil bleeding can lead to a decrease in performance and potentially affect surrounding components.
- Ultra Soft: The softness of a thermal pad is paramount in its ability to conform to the microscopic irregularities between the CPU and heatsink surfaces. Ultra-soft thermal pads can fill in gaps more effectively, ensuring better surface contact and thus improved heat transfer.
- High Compressibility: A highly compressible thermal pad can squash down to fit exactly right into the space it needs to, no matter if that space is big or small. This flexibility makes sure there’s always a tight fit, helping heat transfer better without any gaps.
Challenges of Thermal Pad Thickness on Uneven Surfaces
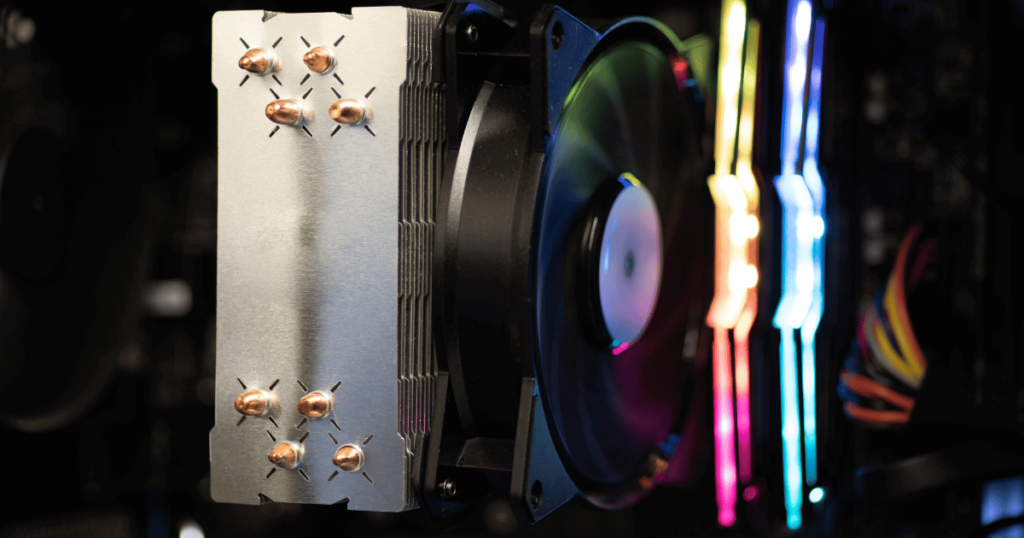
One of the challenges when using thermal pads is their uniform thickness, which can be problematic when addressing the gap between CPUs and their heatsinks. This issue stems from the fact that the surfaces of CPU coolers and CPUs themselves are not perfectly flat but have microscopic gaps and irregularities.
These irregularities mean that while some areas might achieve perfect contact between the CPU and the cooler, other spots reveal varying gap sizes. These gaps are typically microscopic, on the order of a few micrometers, and are usually not visible to the naked eye. Ideally, a thermal pad should conform to these gaps. However, the uniform thickness of thermal pads can lead to an excess of material in areas where the gap is smaller.
While thermal pads are compressible and can deform to fill these gaps, the material itself does not disappear. Therefore, any excess material still present after compression can act as a barrier to heat transfer, effectively reducing the overall heat dissipation from the CPU to the heatsink.
Conclusion
We hope you found this guide on thermal pad heat conductivity useful. Your experiences matter to us, so feel free to drop a comment sharing your encounters with thermal pads.
If you’re interested in learning more, don’t miss our article comparing thermal pads vs thermal paste. And remember, no question is too small or too big, so if you have any queries, don’t hesitate to ask. We’re here to help!
We're an affiliate
We hope you love the products we recommend! Just so you know, gameraround.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by linking to Amazon.com.

