At first glance, all thermal pastes may appear similar in their greasy texture. However, they vary widely in composition and cooling capabilities. This variety means that each type has its own strengths and ideal use cases.
Understanding the different types of thermal paste is your first step toward choosing the right one for your needs.
Let’s explore these variations to help you make an informed decision.
What are the Different Types of Thermal Paste?
Liquid Metal-Based Thermal Paste
Liquid metal-based thermal paste is a distinct type within the metal-based category. Its key component is a blend of liquid metal alloys, including gallium. This unique composition enhances its thermal conductivity, making it up to eight times more effective than traditional thermal pastes.
This exceptional conductivity makes it perfect for tasks like extreme overclocking and handling the demands of high-performance computing.
However, liquid metal-based thermal paste is also very expensive and risky. It is highly electrically conductive, which means it can cause short-circuiting if it spills over to other components. It is also very corrosive. When liquid metal is applied to an aluminum cold plate, it can lead to corrosion, weakening the cold plate over time.
On the other hand, copper heat spreaders may stain and pit when exposed to liquid metal, but their performance remains largely unaffected, and it’s generally safe to use with liquid metal.
Metal-Based Thermal Paste
Similar to the liquid metal-based type, metal-based thermal paste is another great option that also contains metal elements such as aluminum, silver, or copper. It’s highly efficient for transferring heat, leading to superb cooling, especially in high-performance and overclocked systems. This type is thin and easy to spread, requiring only a small amount for effective coverage.
Ideal for demanding computing environments, it withstands high temperatures without degrading. However, like its liquid metal counterpart, it’s electrically conductive and expensive.
Users need to apply it cautiously to avoid potential damage to other components due to its conductivity.
Carbon-Based Thermal Paste

Moving on to carbon-based thermal paste, this type represents a middle ground in thermal conductivity and price.
As its name suggests, carbon-based thermal paste utilizes small carbon fibers, often enhanced with diamond powder, giving it a high level of thermal conductivity. It effectively bridges the gap between ceramic and metal-based pastes, balancing performance and cost.
Though it comes with a slightly higher price tag than ceramic pastes, it’s more affordable than the metal variants. Its standout feature is its low electrical conductivity, making it a safer choice in scenarios where electrical risks are a concern.
Ideal for those who seek advanced cooling performance without the electrical risks associated with metal-based pastes, carbon-based thermal paste presents a compelling middle ground.
Ceramic-Based Thermal Paste
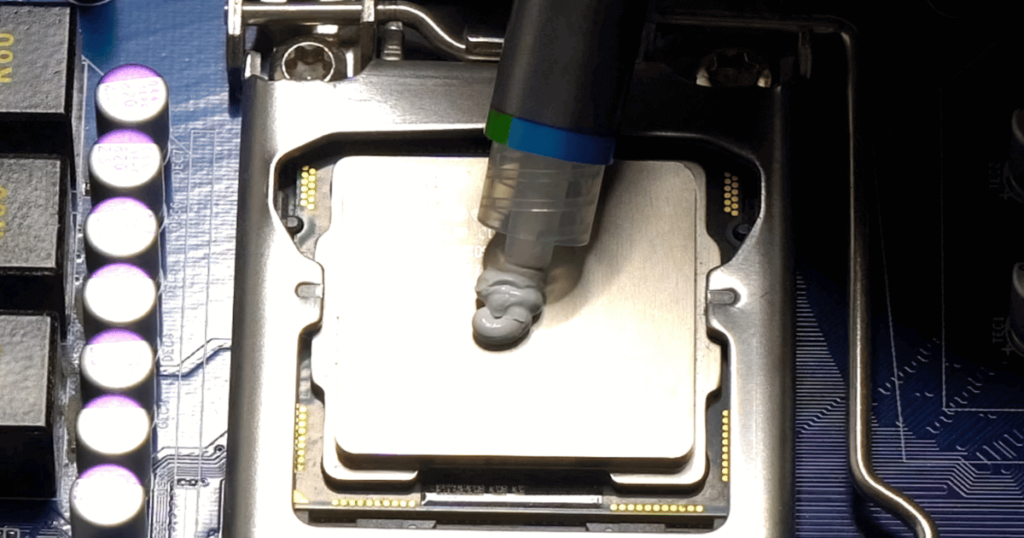
One of the most common and popular types of thermal paste is ceramic-based thermal paste. This type is composed of ceramic particles, such as aluminum oxide or zinc oxide, which are suspended in a silicone oil.
Ceramic-based thermal paste has good thermal conductivity, which means it can transfer heat from the CPU to the heatsink effectively. It is also non-electrically conductive, which means it poses no risk of short-circuiting if it comes into contact with other components.
This type of thermal paste is a great choice for general computing needs, from everyday tasks to gaming. It can handle moderate to high temperatures, and it is relatively easy to apply and remove. It is also affordable and widely available, making it a go-to option for most PC builders.
However, ceramic-based thermal paste is not the best option for extreme overclocking. It is not as effective as liquid metal-based thermal paste, which has a higher thermal conductivity. It also tends to dry out over time, losing its effectiveness and requiring reapplication.
Silicone-Based Thermal Paste

The last type of thermal paste we are going to cover is silicone-based thermal paste. This type is also common in thermal pads. It’s known for being more fluid and can be messier to apply compared to other types.
While it is a budget-friendly option, it doesn’t perform as effectively in heat transfer as ceramic-based pastes. This lesser efficiency is a key reason why some brands specifically market their products as not silicone-based.
Silicone-based paste is generally suited for less demanding thermal management tasks, where high-performance cooling is not a primary requirement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does it matter what kind of thermal paste you use?
Yes, it does matter. Different types of thermal paste have different thermal conductivity, which affects how well they can transfer heat from the CPU to the heatsink. They also have different advantages and disadvantages, such as price, availability, ease of application, durability, and safety.
Does thermal paste expire?
Yes, thermal paste does expire. Most thermal pastes have a shelf life of around 2 years, assuming they are stored properly. Over time, their effectiveness in conducting heat can diminish.
Should I use conductive or non conductive thermal paste?
Non-conductive thermal paste is generally safer, especially for new PC builders. It reduces the risk of electrical shorts in case of accidental spillage on other components.
Conclusion
I hope this guide has given you a clear understanding of the different types of thermal paste and their unique benefits. Now that you’re equipped with this knowledge, you can make a more informed choice for your computer’s cooling needs.
I’d love to hear from you! Drop a comment sharing what type of thermal paste you’ve been using and how it’s working for you. If you have any questions or are still wondering which type is right for you, feel free to ask. While you’re at it, check out article latest article about whether thermal paste is necessary or not.
We're an affiliate
We hope you love the products we recommend! Just so you know, gameraround.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by linking to Amazon.com.

